1. (이진)트리
- 원소들 간에 계층관계를 가지는 계층적 자료구조이다.
- 상위 원소에서 하위 원소로 내려가면서 확장되는 Tree모양의 구조이다.
- 이진트리는 모든 부모노드의 자식노드가 최대 2개만 가지고 있는 트리를 뜻한다.
- 딕셔너리, 세트, 우선순위 큐와 같은 추상자료형을 구현할 수 있다.
- 탐색 알고리즘에 많이 사용된다.
- (이진)트리의 구성요소
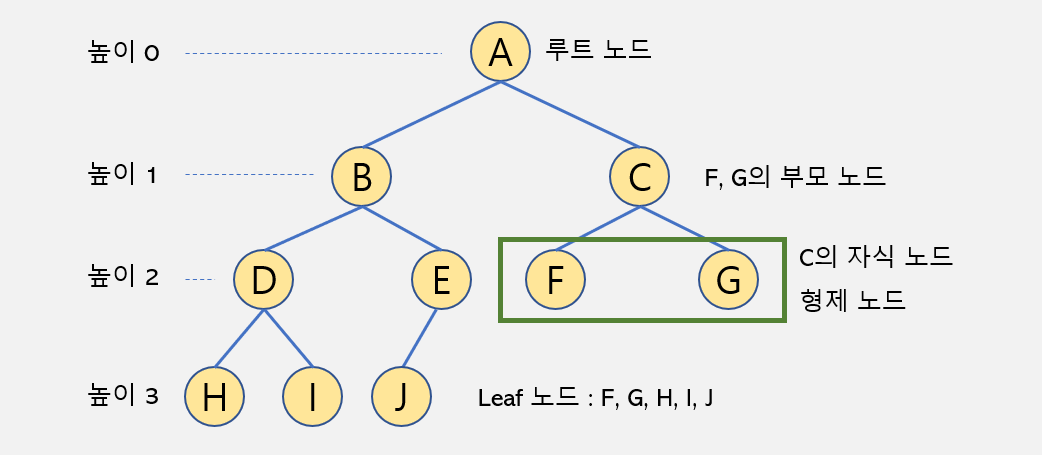
2. 트리의 종류
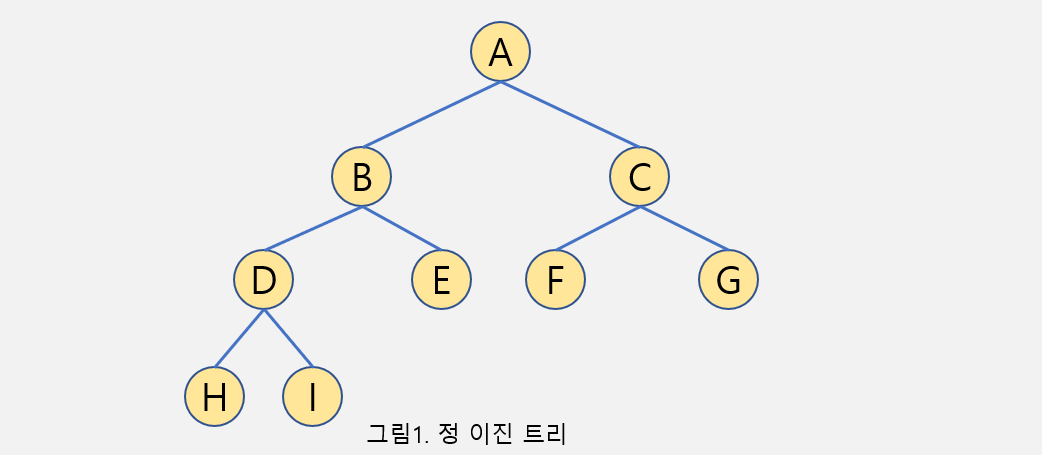
2-1 정 이진 트리 (Full Binary Tree)
-
자식이 0개이거나 2개인 트리 구조
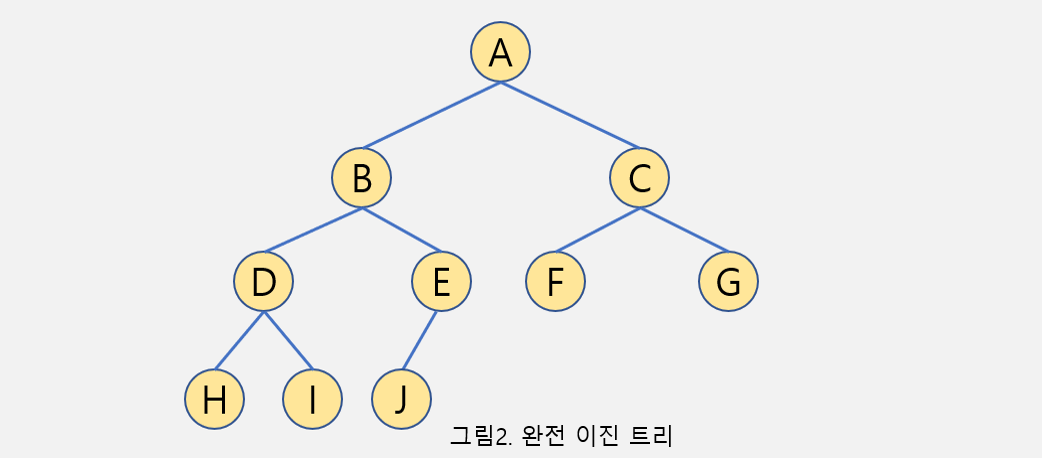
2-2 완전 이진 트리 (Complete Binary Tree) ⭐
- 마지막 높이 이전까지는 모든 노드들이 채워져 있다.
-
마지막 높이의 노드는 왼쪽부터 차례대로 채워져 있다.
- 파이썬 리스트 (동적 배열)로 구현할 수 있습니다.
완전 이진 트리 코드
tree = [None, 1, 5, 12, 11, 9, 10, 14, 2, 10] # 트리 그림을 보고 직접 리스트로 작성 def get_parent_index(complete_binary_tree, index): """배열로 구현한 완전 이진 트리에서 index번째 노드의 부모 노드의 인덱스를 리턴하는 함수""" parent_index = index//2 if complete_binary_tree[parent_index] != None : return parent_index else : return None def get_left_child_index(complete_binary_tree, index): """배열로 구현한 완전 이진 트리에서 index번째 노드의 왼쪽 자식 노드의 인덱스를 리턴하는 함수""" left_child_index = 2*index if len(complete_binary_tree) < left_child_index : return None else: return left_child_index def get_right_child_index(complete_binary_tree, index): """배열로 구현한 완전 이진 트리에서 index번째 노드의 오른쪽 자식 노드의 인덱스를 리턴하는 함수""" right_child_index = 2*index + 1 if len(complete_binary_tree) < right_child_index : return None else : return right_child_index
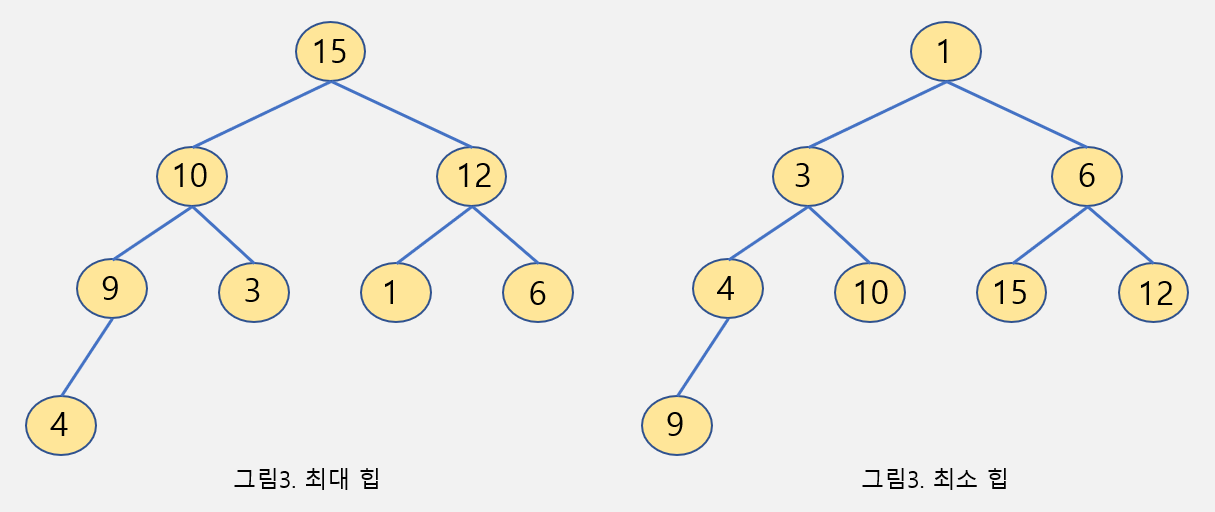
2-3 힙 (Heap) ⭐
- 완전 이진 트리 구조 + 데이터 값이 힙 속성을 따른다.
- 힙 속성: 모든 노드의 데이터는 자식 노드들의 데이터보다 크다(혹은 작다)
- 최대 힙 은 부모 노드가 자식 노드보다 크도록 트리 구조를 만든다.
-
최소 힙 정렬은 부모 노드가 자식 노드보다 작도록 트리 구조를 만든다.
- 힙 정렬 에 이용된다.
- 내림/오름차순 정렬 한다고 했을 때 구현 방법은 다음과 같다.
구현 방법
- 최대/최소 힙을 만든다.
- root와 마지막 노드를 바꿔준다.
- (바꾼 노드는 없는 노드 취급한다)
- 새로운 트리가 힙 속성을 가지도록 heapify를 호출한다.
- 2-4번을 모든 인덱스를 돌 때까지 반복한다.
🔔 heapify : 파라미터로 넣은 노드를 기준으로 밑에 노드들이 모두 힙 속성을 지키도록 하는 함수
힙 정렬 코드
"""heapify""" def swap(tree, index_1, index_2): """완전 이진 트리의 노드 index_1과 노드 index_2의 위치를 바꿔준다""" temp = tree[index_1] tree[index_1] = tree[index_2] tree[index_2] = temp def heapify(tree, index, tree_size): """heapify 함수""" # 왼쪽 자식 노드의 인덱스와 오른쪽 자식 노드의 인덱스를 계산 left_child_index = 2 * index right_child_index = 2 * index + 1 largest = index # 일단 부모 노드의 값이 가장 크다고 설정 # 왼쪽 자식 노드의 값과 비교 if 0 < left_child_index < tree_size and tree[largest] < tree[left_child_index]: largest = left_child_index # 오른쪽 자식 노드의 값과 비교 if 0 < right_child_index < tree_size and tree[largest] < tree[right_child_index]: largest = right_child_index if largest != index: # 부모 노드의 값이 자식 노드의 값보다 작으면 swap(tree, index, largest) # 부모 노드와 최댓값을 가진 자식 노드의 위치를 바꿔준다 return heapify(tree, largest, tree_size) # 자리가 바뀌어 자식 노드가 된 기존의 부모 노드를대상으로 또 heapify 함수를 호출한다 #max_value_index = tree.index(max(tree[index], tree[left_child_index], tree[right_child_index])) """힙 정렬""" def heapsort(tree): """힙 정렬 함수""" tree_size = len(tree) # 마지막 인덱스부터 처음 인덱스까지 heapify를 호출한다 for index in range(tree_size, 0, -1): heapify(tree, index, tree_size) # 마지막 인덱스부터 처음 인덱스까지 for i in range(tree_size-1, 0, -1): swap(tree, 1, i) # root 노드와 마지막 인덱스를 바꿔준 후 heapify(tree, 1, i) # root 노드에 heapify를 호출한다
- 내림/오름차순 정렬 한다고 했을 때 구현 방법은 다음과 같다.
| 정렬 알고리즘 | 시간 복잡도 |
|---|---|
| 선택 정렬 | O(\(n^2\)) |
| 삽입 정렬 | O(\(n^2\)) |
| 합병 정렬 | O(nlg(n)) |
| 퀵 정렬 | 평균 O(nlg(n)) 최악 O(\(n^2\)) |
| 힙 정렬 | O(nlg(n)) |
- 우선 순위 큐 를 구현하는데 이용된다.
- 값이 큰/작은 순서대로 추출된다.
- 구현하는 방법은 다음과 같다.
구현 방법
- 값을 삽입하는 연산을 구현한다.
- 맨 끝에 노드를 추가한다.
- 추가된 노드와 그 부모 노드를 비교해 힙속성을 어기지 않을때까지 바꿔준다.
- 값을 추출하는 연산을 구현한다.
- root와 마지막 노드를 바꿔준다. (root노드의 값이 가장 우선순위가 높은 값)
- 끝으로 온 노드를 트리에서 빼고 리턴해준다.
- root로 온 노드가 힙 속성을 유지하도록 heapify를 호출한다.
🔔 heapify : 파라미터로 넣은 노드를 기준으로 밑에 노드들이 모두 힙 속성을 지키도록 하는 함수
- 값을 삽입하는 연산을 구현한다.
- 트리가 힙 속성을 계속 유지하도록 하면서 삽입 추출 연산을 구현하면 우선 순위 큐로 사용할 수 있다.
우선 순위 큐 코드
def swap(tree, index_1, index_2): """완전 이진 트리의 노드 index_1과 노드 index_2의 위치를 바꿔준다""" temp = tree[index_1] tree[index_1] = tree[index_2] tree[index_2] = temp def heapify(tree, index, tree_size): """heapify 함수""" # 왼쪽 자식 노드의 인덱스와 오른쪽 자식 노드의 인덱스를 계산 left_child_index = 2 * index right_child_index = 2 * index + 1 largest = index # 일단 부모 노드의 값이 가장 크다고 설정 # 왼쪽 자식 노드의 값과 비교 if 0 < left_child_index < tree_size and tree[largest] < tree[left_child_index]: largest = left_child_index # 오른쪽 자식 노드의 값과 비교 if 0 < right_child_index < tree_size and tree[largest] < tree[right_child_index]: largest = right_child_index if largest != index: # 부모 노드의 값이 자식 노드의 값보다 작으면 swap(tree, index, largest) # 부모 노드와 최댓값을 가진 자식 노드의 위치를 바꿔준다 heapify(tree, largest, tree_size) # 자리가 바뀌어 자식 노드가 된 기존의 부모 노드를대상으로 또 heapify 함수를 호출한다 def reverse_heapify(tree, index): """삽입된 노드를 힙 속성을 지키는 위치로 이동시키는 함수""" parent_index = index // 2 # 삽입된 노드의 부모 노드의 인덱스 계산 # 부모 노드가 존재하고, 부모 노드의 값이 삽입된 노드의 값보다 작을 때 if 0 < parent_index < len(tree) and tree[index] > tree[parent_index]: swap(tree, index, parent_index) # 부모 노드와 삽입된 노드의 위치 교환 reverse_heapify(tree, parent_index) # 삽입된 노드를 대상으로 다시 reverse_heapify 호출 class PriorityQueue: """힙으로 구현한 우선순위 큐""" def __init__(self): self.heap = [None] # 파이썬 리스트로 구현한 힙 def insert(self, data): """삽입 메소드""" self.heap.append(data) # 힙의 마지막에 데이터 추가 reverse_heapify(self.heap, len(self.heap)-1) # 삽입된 노드(추가된 데이터)의 위치를 재배치 def extract_max(self): """최고 우선순위 데이터 추출 메소드""" swap(self.heap, 1, len(self.heap) - 1) # root 노드와 마지막 노드의 위치 바꿈 max_value = self.heap.pop() # 힙에서 마지막 노드 추출(삭제)해서 변수에 저장 heapify(self.heap, 1, len(self.heap)) # 새로운 root 노드를 대상으로 heapify 호출해서 힙 속성 유지 return max_value # 최우선순위 데이터 리턴 def __str__(self): return str(self.heap)
| 연산 | 정렬된 동적 배열 | 정렬된 링크드 리스트 | 힙 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 삽입 | O(n) | O(n) | O(lg(n)) |
| 추출 | O(1) | O(1) | O(lg(n)) |
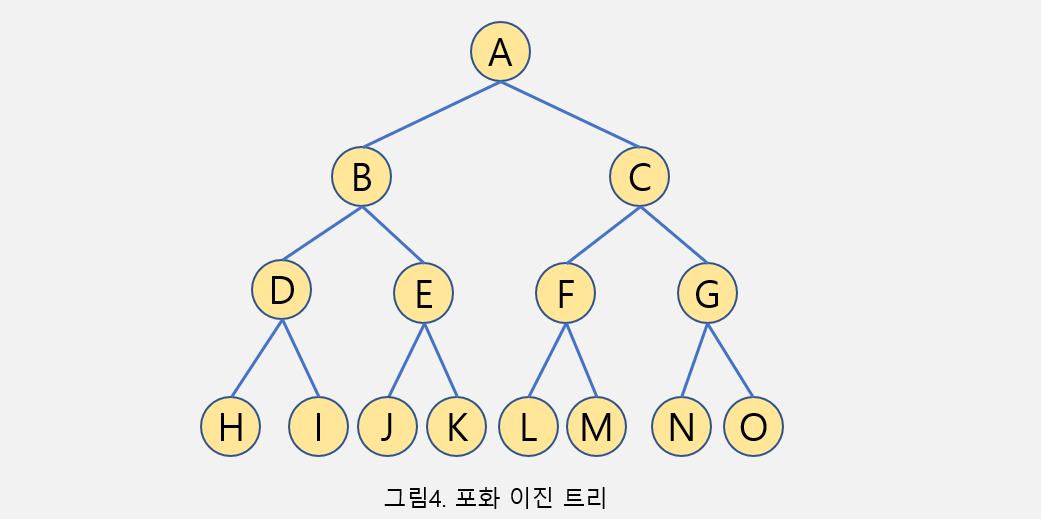
2-4 포화 이진 트리 (Perfect Binary Tree)
-
모든 높이에서 노드가 채워진 트리 구조
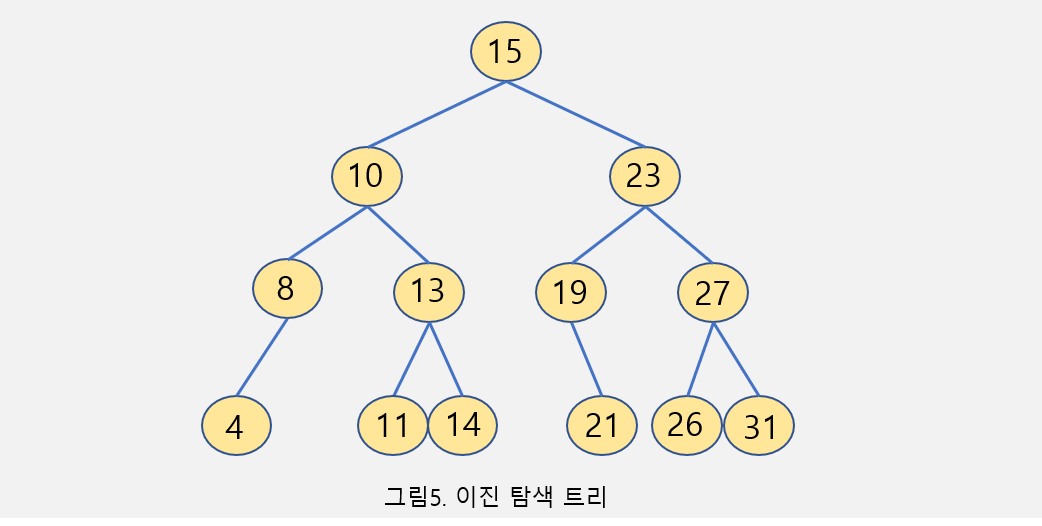
2-5 이진 탐색 트리 (Binary Search Tree) ⭐
- 임의의 노드를 기준으로 왼쪽 자식 노드는 더 작고 오른쪽 자식 노드는 더 크도록 정렬 되어 있는 자료 구조
- 딕셔너리 또는 세트를 구현할 때 사용된다. 하지만 해시 테이블 보다 탐색, 삽입, 삭제 연산의 시간 복잡도가 더 크다.
-
정렬이 필요한 딕셔너리, 세트를 구현할 때 이용된다.
- 탐색/삽입/삭제 코드 구현
이진 탐색 트리 연산 코드
class BinarySearchTree: """이진 탐색 트리 클래스""" def __init__(self): self.root = None """탐색 연산""" def search(self, data): """이진 탐색 트리 탐색 메소드, 찾는 데이터를 갖는 노드가 없으면 None을 리턴한다""" temp = self.root # 탐색용 변수, root 노드로 초기화 # 원하는 데이터를 갖는 노드를 찾을 때까지 돈다 while temp is not None: # 원하는 데이터를 갖는 노드를 찾으면 리턴 if data == temp.data: return temp # 원하는 데이터가 노드의 데이터보다 크면 오른쪽 자식 노드로 간다 if data > temp.data: temp = temp.right_child # 원하는 데이터가 노드의 데이터보다 작으면 왼쪽 자식 노드로 간다 else: temp = temp.left_child return None # 원하는 데이터가 트리에 없으면 None 리턴 """ 삽입 연산""" def insert(self, data): """이진 탐색 트리 삽입 메소드""" new_node = Node(data) # 삽입할 데이터를 갖는 노드 생성 # 트리가 비었으면 새로운 노드를 root 노드로 만든다 if self.root is None: self.root = new_node return temp = self.root # 저장하려는 위치를 찾기 위해 사용할 변수. root 노드로 초기화한다 # 원하는 위치를 찾아간다 while temp is not None: if data > temp.data: # 삽입하려는 데이터가 현재 노드 데이터보다 크다면 # 오른쪽 자식이 없으면 새로운 노드를 현재 노드 오른쪽 자식으로 만듦 if temp.right_child is None: new_node.parent = temp temp.right_child = new_node return # 오른쪽 자식이 있으면 오른쪽 자식으로 간다 else: temp = temp.right_child else: # 삽입하려는 데이터가 현재 노드 데이터보다 작다면 # 왼쪽 자식이 없으면 새로운 노드를 현재 노드 왼쪽 자식으로 만듦 if temp.left_child is None: new_node.parent = temp temp.left_child = new_node return # 왼쪽 자식이 있다면 왼쪽 자식으로 간다 else: temp = temp.left_child @staticmethod def find_min(node): """(부분)이진 탐색 트리의 가장 작은 노드 리턴""" # 코드를 쓰세요 temp = node # 탐색 변수. 파라미터 node로 초기화 # temp가 node를 뿌리로 갖는 부분 트리에서 가장 작은 노드일 때까지 왼쪽 자식 노드로 간다 while temp.left_child is not None: temp = temp.left_child return temp """삭제 연산""" def delete(self, data): """이진 탐색 트리 삭제 메소드""" node_to_delete = self.search(data) # 삭제할 노드를 가지고 온다 parent_node = node_to_delete.parent # 삭제할 노드의 부모 노드 # 경우 1: 지우려는 노드가 leaf 노드일 때 if node_to_delete.left_child is None and node_to_delete.right_child is None: if self.root is node_to_delete: self.root = None else: # 일반적인 경우 if node_to_delete is parent_node.left_child: parent_node.left_child = None else: parent_node.right_child = None # 경우 2: 지우려는 노드가 자식이 하나인 노드일 때: elif node_to_delete.left_child is None: # 지우려는 노드가 오른쪽 자식만 있을 때: # 지우려는 노드가 root 노드일 때 if node_to_delete is self.root: self.root = node_to_delete.right_child self.root.parent = None # 지우려는 노드가 부모의 왼쪽 자식일 때 elif node_to_delete is parent_node.left_child: parent_node.left_child = node_to_delete.right_child node_to_delete.right_child.parent = parent_node # 지우려는 노드가 부모의 오른쪽 자식일 때 else: parent_node.right_child = node_to_delete.right_child node_to_delete.right_child.parent = parent_node elif node_to_delete.right_child is None: # 지우려는 노드가 왼쪽 자식만 있을 때: # 지우려는 노드가 root 노드일 때 if node_to_delete is self.root: self.root = node_to_delete.left_child self.root.parent = None # 지우려는 노드가 부모의 왼쪽 자식일 때 elif node_to_delete is parent_node.left_child: parent_node.left_child = node_to_delete.left_child node_to_delete.left_child.parent = parent_node # 지우려는 노드가 부모의 오른쪽 자식일 때 else: parent_node.right_child = node_to_delete.left_child node_to_delete.left_child.parent = parent_node # 경우 3: 지우려는 노드가 2개의 자식이 있을 때 else: successor = self.find_min(node_to_delete.right_child) # 삭제하려는 노드의 successor 노드 받아오기 node_to_delete.data = successor.data # 삭제하려는 노드의 데이터에 successor의 데이터 저장 # successor 노드 트리에서 삭제 if successor is successor.parent.left_child: # successor 노드가 오른쪽 자식일 때 successor.parent.left_child = successor.right_child else: # successor 노드가 왼쪽 자식일 때 successor.parent.right_child = successor.right_child if successor.right_child is not None: # successor 노드가 오른쪽 자식이 있을 떄 successor.right_child.parent = successor.parent - 평균적으로 이진 탐색 트리의 높이 h는 O(lg(n))이다.
| 연산 | 해시 테이블 | 이진 탐색 트리 |
|---|---|---|
| 탐색 | O(h) (평균적 O(lg(n)), 최악 O(n) | 평균적 O(1), 최악 O(n) |
| 삽입 | O(h) (평균적 O(lg(n)), 최악 O(n) | 평균적 O(1), 최악 O(n) |
| 삭제 | O(h) (평균적 O(lg(n)), 최악 O(n) | 평균적 O(1), 최악 O(n) |
