Hugging face: How do Transformers work?
Huggingface에 관한 포스트는 Huggingface 공식 홈페이지를 참고하여 작성하였으며 그 중에서도 Huggingface를 사용하는 방법에 관해 친절하게 설명해 놓은 글(Huggingface course)이 있어 이것을 바탕으로 작성하였습니다.
이번 포스트에서는 현재 NLP 관련 task에서 모델의 핵심 구조인 Transformer에 대해 배워보겠습니다.🤗
1. A bit of Transformer history
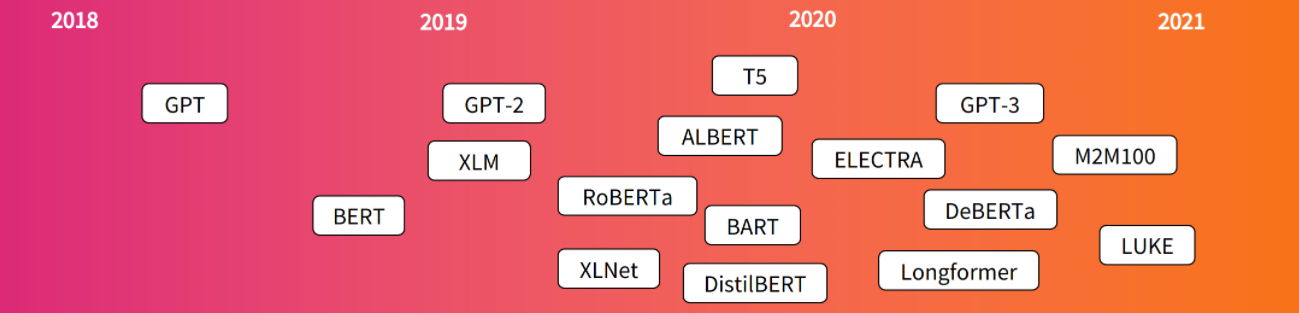
Transformer 구조가 처음 소개된 것은 2017년 6월입니다. 이 당시 Transformer 연구의 task는 번역(translation)에 집중되어 있었습니다. Transformer가 도입된 이후 다양한 task를 수행할 수 있는 관련 모델들이 등장하기 시작했습니다.
- GPT: 트랜스포머 디코더 모델을 이용한 첫 번째 pretrained 모델
- BERT: 트랜스포머의 인코더 모델을 이용한 pretrained 모델
- GPT-2: GPT보다 성능이 더 향상된 모델
- DistilBERT: 모델의 무게를 줄이고 속도를 높이면서 근사한 BERT와 근사한 성능을 보이는 모델
- BART and T5: 원래의 트랜스포머 구조(Encoder-Decoder)를 다시 사용한 모델
- GPT-3: Fine-tuning없이도(called zero-shot learning) 다양한 task에 우수한 성능을 보이는 모델
2. Language model
All the Transformer models mentioned above (GPT, BERT, BART, T5, etc.) have been trained on
large amounts of raw textin a self-supervised fashion.Self-supervised learningis a type of training in which the objective is automatically computed from the inputs of the model. That means that humans are not needed to label the data!
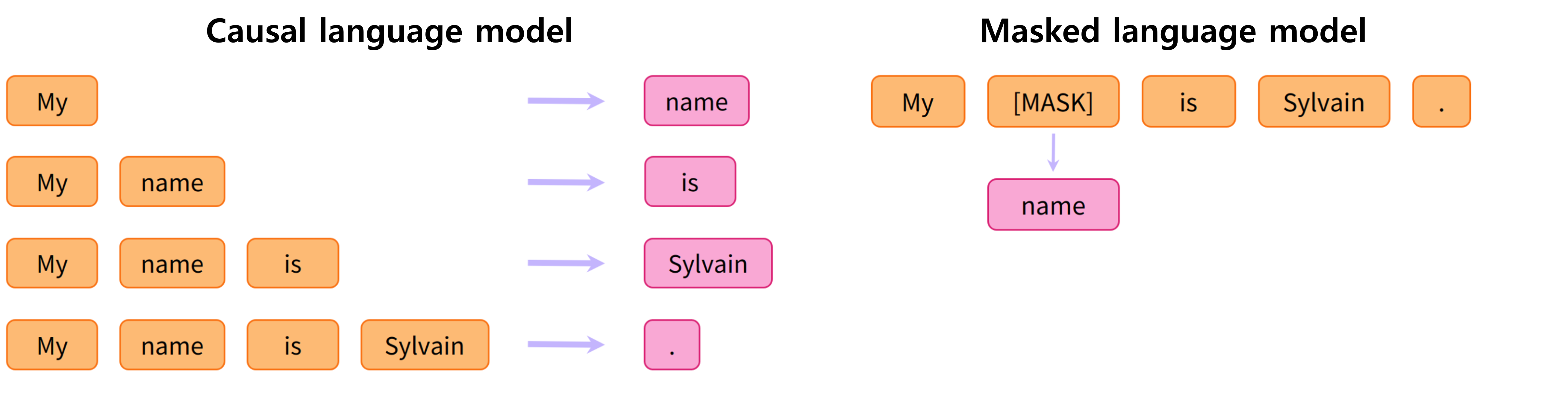
Before, a causal language model has been trained by predicting the next word in a sentence having read the n previous words. it means the output depends on the past and present inputs, but not the future ones.
Another example is masked language model, useful for specific practical tasks.
3. Transfer Learning
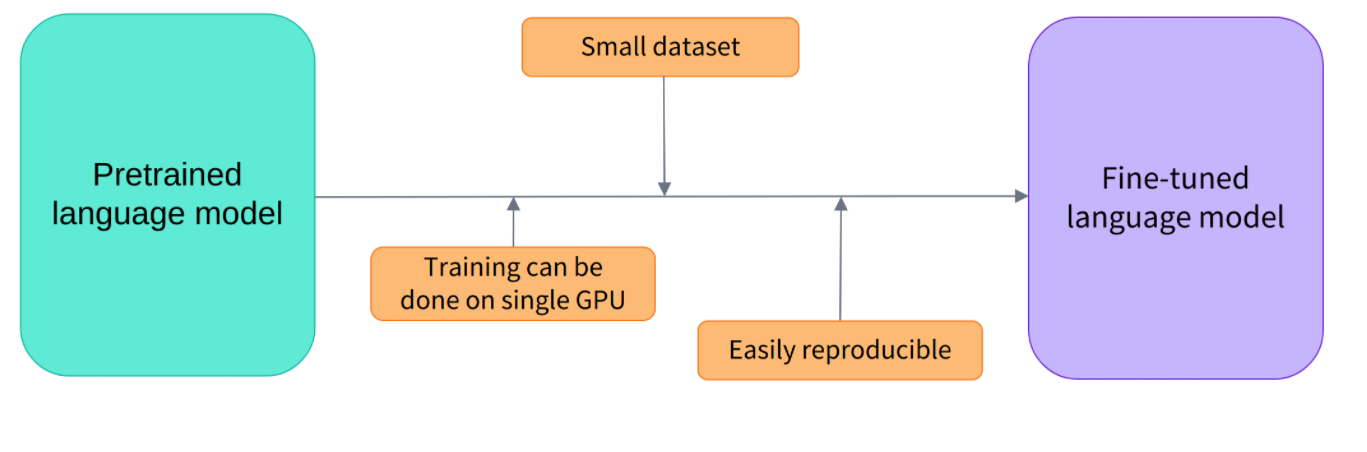
최근에 나오는 언어 모델들(GPT, BERT, BART 등)은 모두 Transfer Learning방법을 이용합니다.
- 엄청난 양의 데이터셋으로 학습된 지식(weights)은 specific task에서 충분히 이점이 있다
- 인프라가 잘 구축된 기업또는 단체에서 제공해주면 개인은 GPU하나로도 충분히 좋은 성능의 모델을 얻을 수 있다
- task마다 구조가 복잡해지지 않는다
4. General Architecture
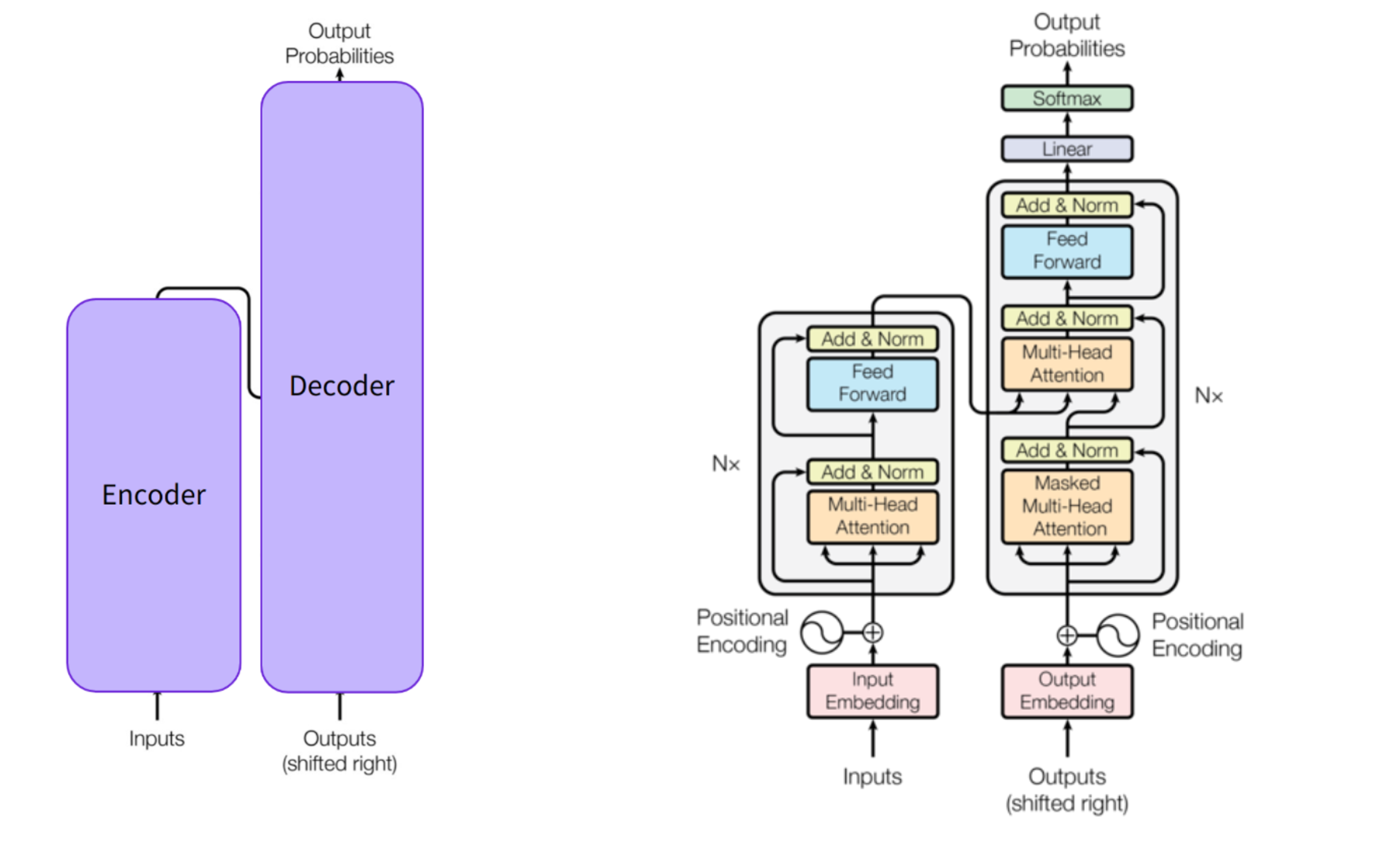
- Encoder: The encoder receives an input and builds a representation of it (its features). This means that the model is optimized to acquire understanding of the input
- Decoder: The decoder uses the encoder’s representation (features) along with other inputs to generate a target sequence. This means that the model is optimized for generating outputs
Each of these parts can be used independently, depending on the task:
- Encoder-only models: Good for tasks that require understanding of the input, such as sentence classification and named entity recognition
- Decoder-only models: Good for generative tasks such as text generation
- Encoder-decoder models : Good for generative tasks that require an input, such as translation or summarization
